What Happens Inside Your Body When You Eat Ghee – Digestion & Metabolism

What Happens When Ghee Enters Your Digestive System
As nutritional science progresses, we are rediscovering what ancient Ayurveda understood thousands of years ago: Pure cow ghee is not just a cooking oil; it is a metabolic catalyst.. In this , we will explore the journey of ghee in your body and why it is the secret weapon for Digestion & sustainable weight loss.
- The Oral and Gastric Phase: The Journey Begins The moment ghee touches your tongue, your body begins to prepare. Unlike heavy vegetable oils or processed butter, ghee has a unique molecular structure. When you eat a spoon full of ghee, it doesn’t behave like your ordinary cooking oil. The moment it enters your mouth, it starts melting and start preparing itself for digestion. As it reaches your stomach, your body automatically recognizes it as a natural fat — not a chemical one. Pure ghee is considered gentle on the digestive system and easy to process.
- Salivary Activation The digestion of fats starts slightly in the mouth with lingual lipase. Since ghee is a clarified fat (meaning the water and milk solids are removed), it sends a signal to the brain that high-quality energy is coming. This triggers the release of bile and gastric juices in anticipation.
Unlike refined oils that slows digestion, where ghee actually supports your stomach by stimulating digestive juices which helps your body break down food more effectively.
How Ghee Is Digested in the Stomach
Stomach Acid Stimulation is one of the main benefits of ghee as it have ability to boost the secretion of gastric acid (HCL).
In the stomach, ghee mixes with bile juice and digestive enzymes. These enzymes break natural fats into smaller particles that your body can easily absorb. Because ghee is a pure fat without additives. Many people experience indigestion due to low stomach acid. Ghee helps balance the stomach’s pH, ensuring that the proteins and carbohydrates you eat with it are broken down more effectively. This prevents the heavy feeling or bloating often linked with fatty meals.
This is why people who suffer from acidity or bloating often feel lighter when they use ghee instead of refined oils.
The Small Intestine: The Nutrient Highway
Once the ghee moves into the small intestine, the real magic happens. Absorption of Fat-Soluble Vitamins.
Your body requires fat to absorb Vitamins A, D, E, and K. You could eat a mountain of spinach or carrots, but without a high-quality carrier fat like ghee, your body will struggle to absorb the fat-soluble phytonutrients. Ghee acts as a “Bio-availability Booster,” ensuring that the nutrients from your entire meal actually reach your bloodstream.
The Power of MCFAs (Medium-Chain Fatty Acids)
Most fats in our diet are Long-Chain Fatty Acids (LCFAs), which require a laborious process of breakdown and transport. Ghee is rich in Medium-Chain Fatty Acids (MCFAs).
- Direct to Liver: MCFAs are absorbed directly by the small intestine and sent to the liver.
- Instant Thermogenesis: Instead of being stored in adipose (fat) tissue, the liver converts these MCFAs into immediate energy. This increases your body’s core temperature slightly—a process called thermogenesis—which helps burn calories even while you are resting.
Role of bile and lipase enzymes
Your liver release bile juice, and your pancreas releases an enzyme called lipase. Together, they break ghee into fatty acids and glycerol. These are then absorbed by your intestines and sent to your cells for energy.
Ghee helps nourishing the lining of your gut, intestine which is important for nutrient absorption and immunity. A healthy gut means less bloating, fewer infections, and better overall health.
Ghee is rich in butyric acid — a fatty acid that feeds the cells of your intestinal wall. This helps heal small damage in the gut and improves digestion. It is one of the reasons ghee is recommended in Ayurveda for people with weak digestion.This is where the magic happens for gut health. Ghee is one of the highest natural sources of Butyric Acid.
Good quality Ghee supports digestion process instead of blocking / delaying it — which is why it feels lighter on stomach.
Ghee is easier to digest than refined oils
Refined oils are chemically processed and also contain bad fat . Your stomach has to work harder to break them down.On the other hand ,Ghee is natural good fat that actually supports your stomach by stimulating digestive juices which helps your body break down food more effectively makes digestion easier and reduces gas, acidity, and heaviness.
Feeding the Microbiome
Your gut is home to trillions of bacteria. Ghee helps create an environment where “good” bacteria thrive. By reducing inflammation and maintaining the mucosal lining, ghee ensures that your microbiome remains balanced, which is directly linked to improved mood and a stronger immune system .It also treats Inflammation as It helps in repairing the gut lining, making it a potent remedy for “Leaky Gut” and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS).
Now Lets Read How Ghee Affects our Metabolism and Help in Fat Burning
Metabolism is the speed at which your body burns calories. Pure Ghee helps improve this process by providing clean, fast-burning fat. Instead of storing it as body fat, your body uses ghee to produce energy. Medium-Chain Fats in Ghee Boost Metabolism.
It may seem confusing to you that how one can eat fat to lose fat, but the science of Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) and Omega-3s in A2 Ghee explains how and why this works.
CLA: The Fat Burner
High-quality A2 cow ghee contains CLA, a fatty acid that has been scientifically shown to:
- Reduce Body Fat Mass: It helps the body prioritize burning stored fat for fuel.
- Increase Lean Muscle: CLA supports the preservation of muscle tissue, which in turn keeps your metabolism high.
Increasing Satiety (The “Fullness” Factor)
One of the biggest hurdles in weight loss is constant hunger. Ghee has a high “Satiety Index.” When you add a teaspoon of ghee to your lunch, it slows down the spike in blood sugar. This prevents the “insulin crash” that usually leads to sugar cravings at 4 PM. By stabilizing your blood sugar, ghee makes it easier to stick to a calorie-controlled diet without feeling deprived.
As these fats don’t require a complex breakdown process. in ghee are quickly converted into energy instead of being stored. These fats go directly to the liver, where they are burned to fuel your body.
Many people think ghee goes straight to the belly. In reality, it helps burn stored fat by improving digestion and metabolism.
Inflammation: It helps repair the gut lining, making it a potent remedy for “Leaky Gut” and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS).
The Metabolism: How Ghee Burns Fat
It sounds counterintuitive, but eating fat can help you lose fat—if it’s the right kind.
| Component | Role in Weight Loss |
| CLA (Conjugated Linoleic Acid) | Known to reduce body fat mass and increase lean muscle. |
| Omega-3 & Omega-9 | Healthy fats that keep you satiated (full) for longer, preventing overeating. |
| Mobilizing Fat | Ghee helps pull fat-soluble toxins out of the cells to be flushed from the body. |
So, Ghee itself doesn’t make you Gain weight .Overeating junk food does. Ghee when eaten with balanced meals ,helps in weight management.
That’s why many weight-loss diets like keto and Ayurveda include ghee — it keeps you full and boosts fat burning.
What Happens to Your Energy, Brain & Hormones
In Ayurveda, ghee is considered a Medhya (brain tonic).
Ghee provide nutrition to Brain as your brain is made of fat, and it needs healthy fat to work properly. It contains Omega 3 healthy fats that support memory, focus, and mental clarity.
Hormones are made from cholesterol.. Ghee provides the necessary healthy cholesterol for the endocrine system to function i.e., Hormonal Balance. For women, this is particularly important for menstrual health and skin elasticity.
Cholesterol is considered as hormone building block
Ghee provides the right kind of cholesterol to keep your hormones balanced.Without good fat, your body cannot make important hormones like estrogen, testosterone & cortisol in adequate amount .Just like its important to keep bad cholesterol low , likewise its important to keep good cholesterol maintained for body functioning . little changes in hormones can make big impact on Mental & physical health.
How to Consume Ghee for Maximum Results
The Morning Ritual (Ushapan)
- How: 1 teaspoon of Shahji A2 Ghee in a cup of warm water or ginger tea on an empty stomach.
- Why: This “lubricates” the digestive tract and flushes out the Ama (toxins) accumulated overnight. It prepares the gallbladder for the day’s digestion.
Cooking at High Heat
- How: Use ghee for sautéing, frying, or roasting.
- Why: Ghee has a very high smoke point (approx. 250°C / 482°F). Unlike olive oil or butter, it doesn’t break down into toxic free radicals when you cook with it at high temperatures.
The Night Dose
- How: 1 teaspoon of ghee in warm A2 milk before bed.
- Why: This acts as a mild natural laxative for those struggling with constipation and helps induce deep, restful sleep.
When you consume a brand like Shahji A2 Pure Cow Ghee, you are not just adding flavor to your meal. You are starting a series of biological processes that influence everything from your brain function to your gut lining.
Summary Table: Ghee vs. Refined Oils
| Feature | Shahji A2 Cow Ghee | Refined Vegetable Oils |
| Digestion | Easy; stimulates HCL | Heavy; slows down digestion |
| Gut Health | Rich in Butyric Acid (Heals) | High in Omega-6 (Inflames) |
| Weight Loss | CLA helps burn fat | Linked to fat storage |
| Smoke Point | Very High (250°C) | Low (Breaks down into toxins) |
| Vitamins | High in A, D, E, K | None (Synthetic vitamins added) |
Choose the Right Ghee for Your Body
If you want to experience the full benefits of healthy digestion, better metabolism, and sustained energy, quality matters more than quantity. Traditional Bilona-made A2 ghee from indigenous Indian breeds contains higher butyric acid, CLA, and natural fat-soluble vitamins compared to mass-produced or refined fats.
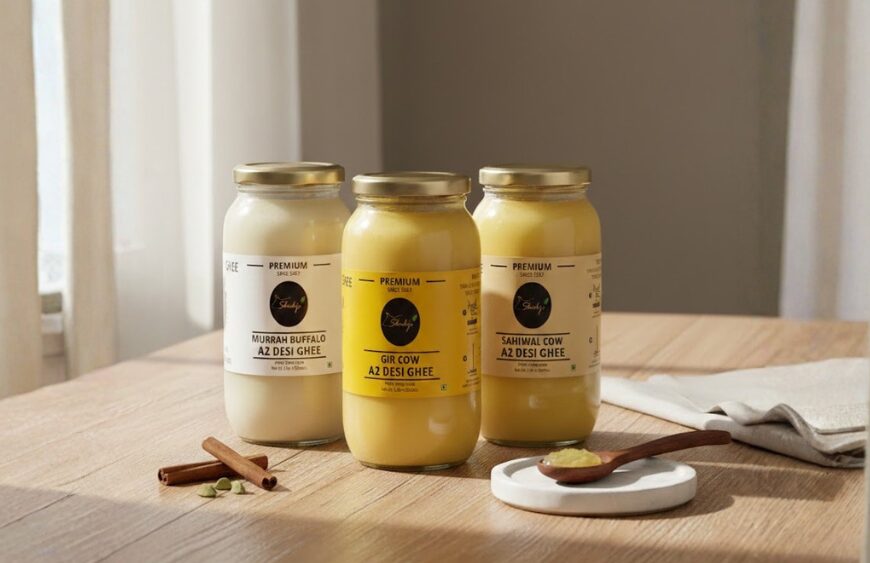

At Shahji Ghee, we prepare small-batch, slow-churned ghee using the classical Bilona method to preserve nutrients and digestibility.
- A2 Gir Cow Ghee
Light, aromatic, and easy to digest. Ideal for gut repair and children or seniors with sensitive digestion.
https://shahjighee.com/product/a2-gir-cow-ghee - A2 Sahiwal Cow Ghee
Richer in flavor with higher nutritional density. Supports immunity, strength, and long-lasting energy.
https://shahjighee.com/product/a2-cow-ghee - Murrah Buffalo Ghee
Creamier and more satiating with higher fat content. Provides sustained energy and longer fullness.
https://shahjighee.com/product/buffalo-ghee
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Does ghee increase Bad Cholesterol (LDL)?
Recent studies show that when consumed in moderation (1-2 teaspoons a day), ghee can actually improve the ratio of HDL (good) to LDL (bad) cholesterol. The MCFAs in ghee do not contribute to arterial clogging like the trans-fats found in processed foods.
Is ghee better than butter?
Ghee is butter that has been “clarified.” This means it is free from lactose and casein, making it superior for people with dairy sensitivities. It also has a much higher smoke point than butter.
Can ghee help with joint pain?
Yes. Ayurveda refers to this as Snehana. Ghee acts as an internal lubricant for the joints and reduces systemic inflammation, which is often the root cause of arthritis and stiffness.
If you are looking to lose weight or simply improve your gut health, don’t fear the fat. Embrace the ancient wisdom of A2 Ghee and give your body the premium fuel it deserves.
Further Reading & References
Scientific & Regulatory Sources
- FSSAI – Indian Food Safety Standards for Ghee
Official standards defining purity, composition, and quality parameters for ghee in India.
https://www.fssai.gov.in - Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) – Dairy Science
Scientific studies on dairy digestion, fat metabolism, and livestock nutrition.
https://icar.org.in - FAO – Dairy Fat Nutrition Reports
Global research on milk fats, CLA, and metabolic benefits.
https://www.fao.org/home/en
Written by & updated
Written by: Shahji Ghee Knowledge Team
Last Updated: January, 2026